Assessment of Drinking Water Quality of Sheikhupura City
Keywords:
Drinking water quality, Sheikhupura city, physical parameters, chemical parameters, biological parametersAbstract
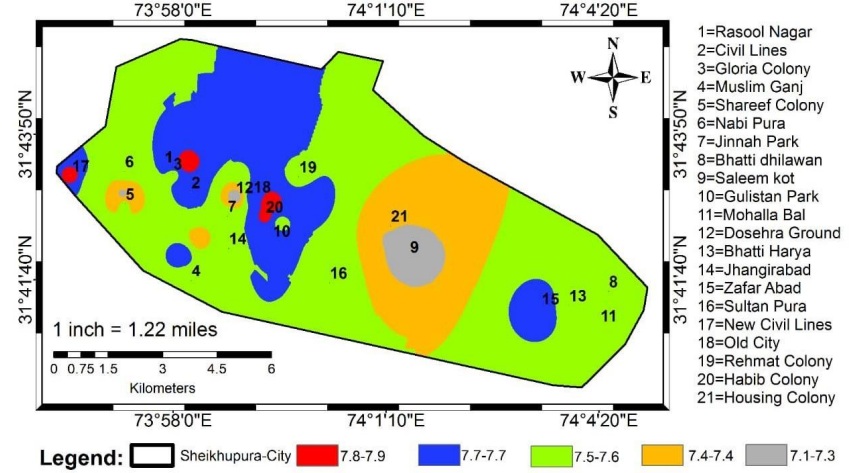
Assessment of water quality is essential to get rid of water borne diseases not only for humans but also for other organisms. Production of healthy grains is largely dependent upon provision of high-quality water to seasonal crops. A study was carried out to assess the drinking water quality of district Sheikhupura. The water samples were collected from twenty-one different locations of the city. The areas of the city where population density was higher more than one water samples were collected from there and after analysis most polluted areas were highlighted. Sixteen physiochemical parameters (pH, taste, odor, color, temperature, turbidity, total dissolved solids, total hardness, calcium, magnesium, alkalinity, chloride, electrical conductivity, arsenic, iron, fluoride and sulphate) and one biological parameter (total coliform) were tested for each sample site and the results were compared with World Health Organization (WHO) predefined standard of drinking water to highlight the vulnerable sites having water quality below WHO standards. Based on physiochemical parameter results, the water samples of ten different locations were found unfit for human consumption and for agriculture as well. The presence of brown and green particles were found in two samples, whereas the value of total dissolved solids was higher than the permissible limit at fivesample site and the value of arsenic was higher than the limit at three different sites. Only one water sample which was collected from Housing Colony was found biologically fit whereas other thirty-one samples were found biologically contaminated. The possible cause of this contamination was the mixing of wastewater with ground water. It is recommended that the water should be used after boiling or compulsory chlorination should be performed to eliminate biological contamination.