Advancements in Precision Fertilization Technologies and Controlled-Dispersion Fertilizers for Sustainable Rice Cultivation
Keywords:
Sustainable Agricultural Development, Chemical Fertilizers, Coating Materials, Fertilization TechnologiesAbstract
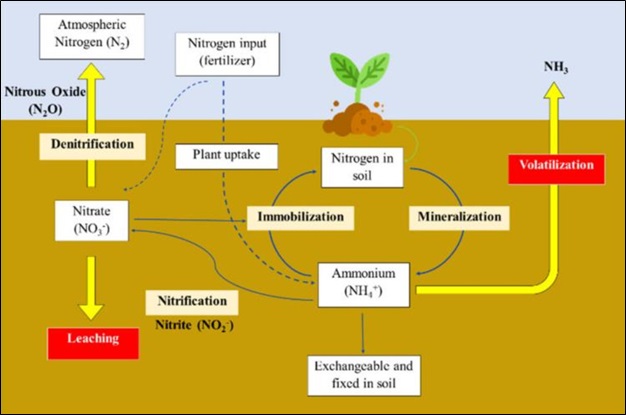
World hunger remains a persistent challenge, necessitating sustainable agricultural strategies to address food demands. Efficient fertilizer use in rice cultivation is identified as a key contributor to sustainable agricultural development. The study introduces precision side-depth fertilization application technology for direct-seeded rice, optimizing fertilization processes and enhancing efficiency. The research explores various side depth fertilizer application devices, focusing on their ability to seamlessly combine precision and depth. The proposed intermittent fixed-point precision method and device aim to meet side depth fertilization requirements, addressing these challenges. In the context of increasing demand for food production, driven by population growth, the paper discusses the limitations of conventional fertilizers. Excessive use of chemical fertilizers results in challenges such as high production costs, resource depletion, and environmental pollution. To break this cycle, the study emphasizes deep fertilization technology, strategically applying fertilizers at specific depths during crop growth. The impact of fertilizer discharge devices on uniformity is crucial in mechanized farming. To enhance crop yields, the application of fertilizers is essential. Traditional manual fertilization methods in paddy rice cultivation are labor-intensive and inefficient. The study advocates for the mechanization of fertilizer application, considering the mechanical and physical properties of fertilizers. The research investigates the effects of particle size distribution and fertilizer concentration on flow parameters, contributing to the design of effective fertilizer application machines. The paper addresses the limitations of conventional fertilizers, emphasizing the environmental concerns associated with nitrogen-based fertilizers. ControlledDispersion Fertilizers (CDFs), particularly those with hydrogel coatings, emerge as a promising solution. The study categorizes coating materials into inorganic, synthetic polymer-based, natural polymer-based, and other organic materials, providing insights into their effectiveness. In conclusion, the paper underscores the significance of precision fertilization technologies, deep fertilization methods, and Controlled-Dispersion Fertilizers in promoting sustainable agricultural practices and addressing global food security.