Health Risk Factors for Incidence of Dengue Virus Infection in Different Districts of Punjab, Pakistan
Keywords:
Dengue Fever , Human Health, Hazards , Punjab, PakistanAbstract
Background:
Dengue fever is one of the major threats all over the world. A positive-stranded RNA virus that belongs to the family Flaviviride, known as DENV is the etiological agent of dengue fever among humans. It is a mosquito-borne viral disease in humans which is spread by female Aedes mosquito. Female mosquito feeds on blood to mature their eggs and during their meal, they transmit the virus from infected to healthy individuals by biting. This disease is now an emerging threat in Pakistan.
Objectives:
The present study aimed to explore health risk factors for dengue fever in addition to their demographic status (age, gender, occupation, and educational level), daily work activity (sedentary or non-sedentary), and residential status (nature of house, location of house).
Material and Methodology:
The data was collected from 31 districts of Punjab Pakistan. Demographic data of all the patients was collected in a questionnaire-based Performa. The age group of different patients and the prevalence of dengue fever were correlated with each other at P < 0.05 by the Two-Way ANOVA Test (α significance at 0.05).
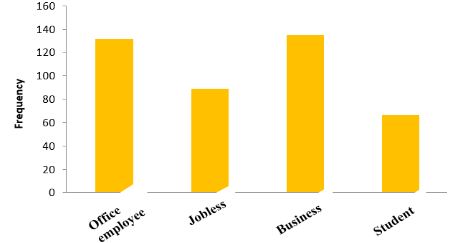
Results:
The data was collected from 31 districts of Punjab in questionnaire-based Performa. The study was conducted under ERC No 892 by the Ethics Review Committee of the Department of Biology, PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Out of 423 patients present in District Headquarters (DHQs) hospitals in different districts of Punjab, 263 were females which compose 62% of the total affected population and 160 were males which composed 38% males were found to be the total affected population. Most of the affected females were aged between 39-47 years however most of the males were from age groups of 30-38 years.
Conclusion:
Obtained data revealed that low socioeconomic status and crowded houses with poor ventilation systems make people prone to infection. Moreover, uncovered water containers and animal/plant pots were recorded as significant indoor breeding sites for mosquitoes. However, water reservoirs and vegetation around the house were significant outdoor breeding sites.