Ethno Pharmacological Profile of Weed Flora of Thanda Paani Village, Islamabad Pakistan
Keywords:
Ethno-botany, , Most Common Families, Predominant Medicinal Plants, Thanda Pani, IslamabadAbstract
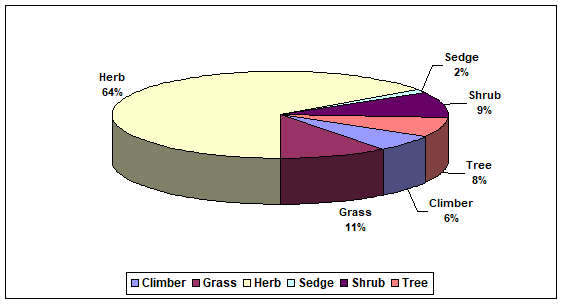
A study was conducted in Thanda Paani to enlist the wild plant species. The people of the area have to use these plants for various purposes and have for a long time been dependent on surrounding plant resources for their food, shelter, fodder, health, care, and other cultural purposes. The present study reported 66 plant species belonging to 59 genera and 29 families. The detailed inventory includes botanical names, vernacular names, part used, specimen No, medicinal, and other uses. To determine the biodiversity of plant species, there were six habits of flora and out of which were herbs (43 spp., 65%), grasses (7 spp., 11%), shrubs (6 spp., 9%), trees (5 spp., 8%), climbers (4 spp., 6%), and sedge (1 spp., 2%). Furthermore, the One-Way ANOVA Test was used to determine the significance of plant species. The P value of 5.57E-31 which is less than 0.05 indicated that plant species have a positive relationship between them. The ecological relationship between different plant species was determined using Tukey's HSD test. This test was used to determine the relationship between the groups of the samples. The results of the wild plant species in this area showed that they have a strong correlation between them and they support each other in this environment naturally. Herbs used both in traditional and allopathic medicine are now being commercially exploited for various compounds; therefore, more research is warranted and its conservation has become necessary.