Assessing Climate-Smart Practice Adoption in Farm Households: A Binary Analysis
Keywords:
Climate-Smart Agriculture, Econometric Framework, Agricultural Parameters, Statistical validation.Abstract
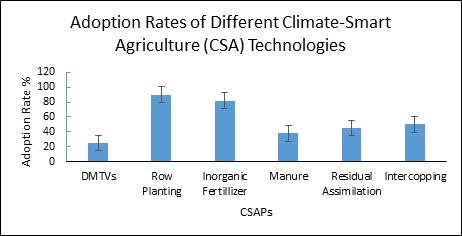
This study investigates the impact of Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) technology adoption on farm performance among maize farmers in the Sialkot and Punjab regions of Pakistan. Utilizing a cross-sectional design and data collected from 320 maize farmers during August to September 2023, the study employs a multistage sampling technique to ensure representation across socio-economic and agricultural parameters. An econometric framework based on the Multinomial Endogenous Switching Regression (MESR) model is used to address self-selection biases in adoption decisions and estimate treatment effects robustly. Data includes socio-economic characteristics, agricultural data, access to CSA technology information, and institutional factors, with maize yields and net farm income as outcome variables. The analysis comprises a Multinomial Logit (MNL) model to identify factors influencing CSA technology adoption and DTMV approach to examine relationships between explanatory variables and outcomes for adopters and non-adopters. Statistical validation of instrumental variables is conducted, and the results are interpreted to provide insights for agricultural development policy in Pakistan.